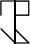Tool to convert Cistercian numbers (read / write monks cipher/numbers of cistercian monks into Arabic numerals) used in the Middle Ages (also called cipher of the monks).
Cistercian Monk Numerals - dCode
Tag(s) : Numeral System, Symbol Substitution
dCode is free and its tools are a valuable help in games, maths, geocaching, puzzles and problems to solve every day!
A suggestion ? a feedback ? a bug ? an idea ? Write to dCode!
Cistercian Monk Numerals
Conversion of Cistercian Numbers
Convert to Cistercian Number
Answers to Questions (FAQ)
What are cistercian numbers? (Definition)
Cistercian numeration is a medieval system used by Cistercian monks between the 13th and 15th centuries. It allows any number from 0 to 9999 to be represented using a single symbol consisting of a vertical bar with a few added strokes around it. This system has recently been rediscovered and studied, notably by historian David A. King.
How to write a number with cistercian monks cipher?
Cistercian numerals are constructed from a central vertical bar, around which lines are placed in four quadrants.
— ↗ Top right: units
— ↖ Top left: tens
— ↘ Bottom right: hundreds
— ↙ Bottom left: thousands
Each digit from 1 to 9 has a basic symbol (made up of small lines). The 0 has no symbol (the quadrant remains empty).
| 1 | .png) | 2 | .png) | 3 | .png) |
| 4 | .png) | 5 | .png) | 6 | .png) |
| 7 | .png) | 8 | .png) | 9 | .png) |
To compose a multi-digit number, place the symbol in the corresponding quadrant, adjusting it by rotation or symmetry.
The result is a single symbol combining these elements around the central vertical line.
How to read/convert a cistercian number to arabic number?
What was the use of this numbering?
Cistercian numeration was not intended for calculations or accounting. It was mainly used to identify and organize elements in manuscripts: page numbering, year markers, text divisions, lists or tables.
How to write a decimal number (with decimal places)?
There is no evidence that Cistercian monks used decimal numbers. Their system was primarily used to record whole numbers, particularly for chronological references.
There is no evidence that they adapted this notation to fractions or decimal measurements.
How to recognize a cistercian monk cipher/numbers?
A Cistercian number is easily recognized by its shape: a central line surrounded by small lines in the four corners.
All references to the Cistercian order and monks are clues.
This numbering system was brought to light by David A. King's book entitled The Ciphers of the Monks: a Forgotten Number-notation of the Middle Ages
When was this cistercian numeral system invented?
The cistercian numeral system seems to have been created around the 14th century.
Source code
dCode retains ownership of the "Cistercian Monk Numerals" source code. Any algorithm for the "Cistercian Monk Numerals" algorithm, applet or snippet or script (converter, solver, encryption / decryption, encoding / decoding, ciphering / deciphering, breaker, translator), or any "Cistercian Monk Numerals" functions (calculate, convert, solve, decrypt / encrypt, decipher / cipher, decode / encode, translate) written in any informatic language (Python, Java, PHP, C#, Javascript, Matlab, etc.) or any database download or API access for "Cistercian Monk Numerals" or any other element are not public (except explicit open source licence). Same with the download for offline use on PC, mobile, tablet, iPhone or Android app.
Reminder: dCode is an educational and teaching resource, accessible online for free and for everyone.
Cite dCode
The content of the page "Cistercian Monk Numerals" and its results may be freely copied and reused, including for commercial purposes, provided that dCode.fr is cited as the source (Creative Commons CC-BY free distribution license).
Exporting the results is free and can be done simply by clicking on the export icons ⤓ (.csv or .txt format) or ⧉ (copy and paste).
To cite dCode.fr on another website, use the link:
In a scientific article or book, the recommended bibliographic citation is: Cistercian Monk Numerals on dCode.fr [online website], retrieved on 2026-02-06,
- Conversion of Cistercian Numbers
- Convert to Cistercian Number
- What are cistercian numbers? (Definition)
- How to write a number with cistercian monks cipher?
- How to read/convert a cistercian number to arabic number?
- What was the use of this numbering?
- How to write a decimal number (with decimal places)?
- How to recognize a cistercian monk cipher/numbers?
- When was this cistercian numeral system invented?