Tools to write/translate Braille. Braille is a tactile alphabet/writing system for blind people that also can be described with digits.
Braille Alphabet - dCode
Tag(s) : Communication System, Symbol Substitution
dCode is free and its tools are a valuable help in games, maths, geocaching, puzzles and problems to solve every day!
A suggestion ? a feedback ? a bug ? an idea ? Write to dCode!
Braille Alphabet
Braille Decoder
Braille Encoder
Answers to Questions (FAQ)
What is Braille? (Definition)
The Braille alphabet is a tactile reading system designed for people who are blind or have a visual impairment.
How to encrypt using Braille cipher?
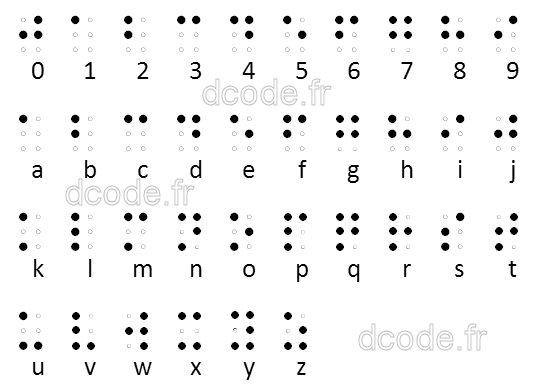
Braille code translation uses a specific alphabet for the visually impaired/blind, made up of raised dots suitable for touch with 1 or more fingers. Each character therefore corresponds to a combination of 6 points (embossed or not) arranged in two columns of three points each.
There are different alphabets, all based on the French alphabet (first created by Louis Braille). Today, the International alphabet is the most widely used.
| A | ⠁ | B | ⠃ | C | ⠉ | D | ⠙ | E | ⠑ | F | ⠋ | G | ⠛ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | ⠓ | I | ⠊ | J | ⠚ | K | ⠅ | L | ⠇ | M | ⠍ | N | ⠝ |
| O | ⠕ | P | ⠏ | Q | ⠟ | R | ⠗ | S | ⠎ | T | ⠞ | U | ⠥ |
| V | ⠧ | W | ⠺ | X | ⠭ | Y | ⠽ | Z | ⠵ |
Example: BRAILLE is written '⠃ ⠗ ⠁ ⠊ ⠇ ⠇ ⠑' (Unicode characters) or .png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png) (images)
(images)
The dots are read in column and are numbered 1-2-3 for the first column and 4-5-6 for the second.
Example: BRAILLE can therefore also be written 12,1235,1,24,123,123,15
For the digits, there are 2 modes, the international mode uses the symbol ⠼ (3-4-5-6 - backward L) and the letters from A to J are respectively 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 and 0. The second French mode, called Antoine, uses the symbol ⠠ (6) instead of ⠼ but keeps the letters from A to J for the value of the digits.
Example: 1 is thus written ⠼⠁ (international mode) or ⠠⠁ (Antoine mode)
An ambiguity can arise on the interpretation of the numbers with several digits '⠼⠁ ⠁' can mean 11 or 1A, to avoid this the numeric symbol ⠼ can be repeated with each digit.
How to decrypt Braille cipher?
How to recognize Braille ciphertext?
The ciphered message is constituted of dots arranged in 2 columns of 3 dots. Caution, however, it may be presented in forms unsuited to tactile reading (see variants).
What are the variants of the Braille cipher?
Depending on the languages some rare characters like those with accents can become other characters.
Braille can be presented in Unicode characters, in numeric code (composed of numbers from 1 to 6 in groups), or in binary format (each digit from 1 to 6 can be rated by a bit 0 or 1).
Example: D is coded 145 or 100110 (bits 1,4,5 are at 1, starting from the left)
The 6 bits can be used in octal format (reverse reading in groups of 3 001 for 1, 011 for 3 to get 13).
How to print Braille?
Braille printing can be done with an embosser. More recently, 3D printing, although much longer, allows you to make your own braille prints.
According to the Braille Authority, a Braille dot must have a diameter of 1.44 mm and a height of 0.48 mm.
The distance between 2 points of the same character (horizontally or vertically) must be 2.34 mm. While the center distance between 2 identical points of 2 consecutive characters must be 6.20 mm. here
When was Braille alphabet invented?
Louis Braille presented its alphabet in 1829.
Source code
dCode retains ownership of the "Braille Alphabet" source code. Any algorithm for the "Braille Alphabet" algorithm, applet or snippet or script (converter, solver, encryption / decryption, encoding / decoding, ciphering / deciphering, breaker, translator), or any "Braille Alphabet" functions (calculate, convert, solve, decrypt / encrypt, decipher / cipher, decode / encode, translate) written in any informatic language (Python, Java, PHP, C#, Javascript, Matlab, etc.) or any database download or API access for "Braille Alphabet" or any other element are not public (except explicit open source licence). Same with the download for offline use on PC, mobile, tablet, iPhone or Android app.
Reminder: dCode is an educational and teaching resource, accessible online for free and for everyone.
Cite dCode
The content of the page "Braille Alphabet" and its results may be freely copied and reused, including for commercial purposes, provided that dCode.fr is cited as the source (Creative Commons CC-BY free distribution license).
Exporting the results is free and can be done simply by clicking on the export icons ⤓ (.csv or .txt format) or ⧉ (copy and paste).
To cite dCode.fr on another website, use the link:
In a scientific article or book, the recommended bibliographic citation is: Braille Alphabet on dCode.fr [online website], retrieved on 2026-02-14,

.png)
.png)
.png)